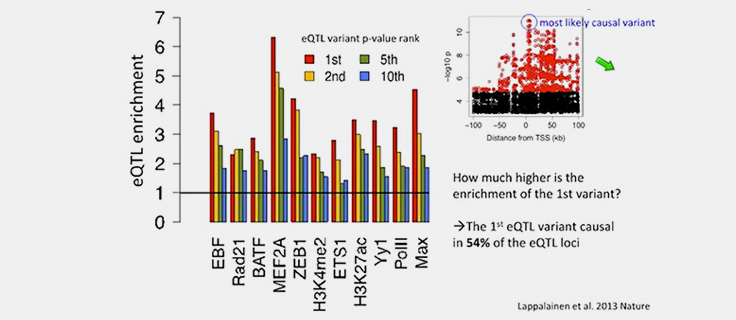
Causal Variant Discovery
Introduction to Causal Variant Discovery
High-throughput genomic technologies enable researchers to screen large sample numbers quickly to find disease-related causal variants. Many single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and copy number variations (CNVs) are associated with disease.
Causal variant identification can lead to further studies of gene targets to characterize disease mechanisms.
SNP Genotyping to Identify Causal Variants
Large-scale investigations of the genome can be performed using arrays or next-generation sequencing (NGS). These surveys can generate statistically significant disease associations and identify potential causal variants of interest for future studies.
Identifying SNPs Using Arrays
Large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using arrays enable you to interrogate tens of thousands of samples at one time. GWAS are effective for identifying common variants associated with disease, uncovering multiple genes for further study.
Identifying SNPs Using NGS
While arrays are effective for finding common variants, they are limited in detecting rare variants. Whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing are common approaches for finding causal variants in rare or complex disease cases. Sequencing individuals or trios is a sensitive, unbiased approach to variant detection that can potentially reveal more variants than array-based approaches.
Complex Disease Research
Genomic technologies are introducing new avenues for understanding complex disease etiology on a molecular level.
Learn More

CNV Detection for Causal Variant Discovery
CNVs are genomic alterations that result in an abnormal number of copies of one or more genes. They are usually caused by structural rearrangements. Like SNPs, certain CNVs have been associated with disease susceptibility.
Detecting CNVs Using Arrays
Array-based approaches for detecting de novo CNVs (not present in or transmitted by either parent) offer efficient and reliable large-scale analysis. You can profile genomic variations such as amplifications, deletions, rearrangements, and copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity.
Illumina offers several types of array solutions for CNV detection, to facilitate causal variant discovery:
- The CytoSNP-850K BeadChip provides comprehensive coverage of cytogenetically relevant genes correlated with high disease risk.
- Human genotyping arrays make cost-effective, large-scale genome-wide and phenome-wide association studies possible.
Detecting CNVs Using NGS
While efficient for large CNV detection, genotyping arrays are less sensitive for small CNVs (< 50 kilobases). NGS offers base-pair resolution that can detect the small CNVs missed by arrays. This knowledge can be useful for studies of missing heritability in complex diseases. The high resolution of sequencing complements the high throughput of arrays, enabling a complete view of the genome.
Recent Developments in Disease Research
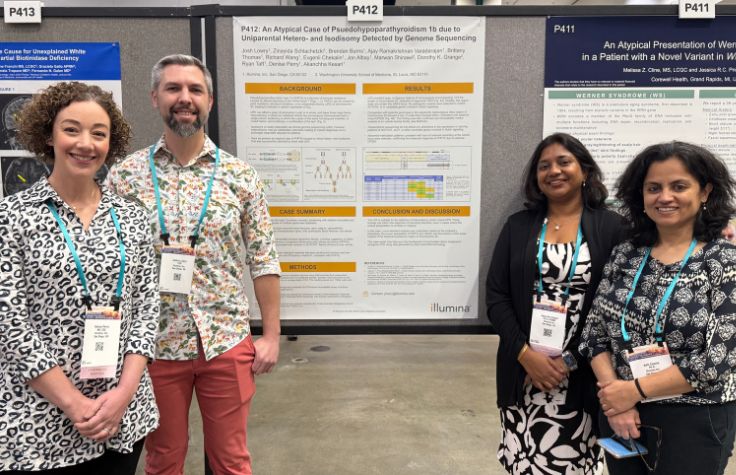

Interrogating challenging genomic regions provides new answers for patients
At ACMG 2025, Illumina demonstrates how whole-genome sequencing and improved bioinformatics has solved cases of rare genetic disease
Read article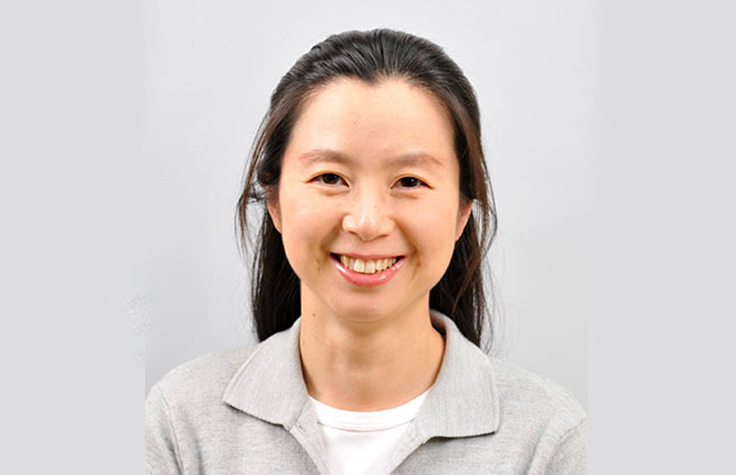
FMRI achieves higher efficiency in genomic research with Illumina’s new exome enrichment
Ms. Sookyoung Kim, the Chief Researcher, Future Medicine Research Institute discusses the results of her evaluation of Illumina DNA Prep with Exome 2.0 Plus Enrichment.
Read Interview
Celebrating discovery and progress in human genetics
In Berlin, Illumina experts and other industry leaders gather at ESHG 2024 to discuss the future of precision medicine and more
Read articleInterested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information from Illumina based on your area of interest? Sign up now.
Related Links
Target Enrichment
Reliably sequence exomes or large numbers of genes (e.g. > 50 genes) using robust hybridization-based enrichment workflows.
Pharmacogenomics and Cardiovascular Disease
See how researchers used an Illumina microarray to identify responder genotypes in a failed cholesterol drug trial.
Genome-Wide Association Studies
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) enable researchers to scan entire genomes of large numbers of subjects quickly in order to find disease-associated variants.