Exome Sequencing
What is whole-exome sequencing?
Whole-exome sequencing, also known as exome sequencing, is a widely used next-generation sequencing (NGS) method that involves sequencing the protein-coding regions of the genome. The human exome represents less than 2% of the genome, but contains ~85% of known disease-related variants,1 making this method a cost-effective alternative to whole-genome sequencing.
Exome sequencing using exome enrichment can efficiently identify coding variants across a broad range of applications, including population genetics, genetic and complex disease research, and cancer studies.
Whole-exome sequencing in 3 simple steps
Investigate the protein-coding regions of the genome with a comprehensive workflow solution.
Advantages of whole-exome sequencing
- Identifies variants across a wide range of applications
- Achieves comprehensive coverage of coding regions
- Provides a cost-effective alternative to whole-genome sequencing (WGS), with 4–5 Gb of sequencing per whole human exome compared to ~90 Gb per whole human genome
- Produces a smaller, more manageable data set for faster, easier data analysis compared to WGS approaches

Efficient analysis of coding regions
Exome sequencing is a cost-effective approach when whole-genome sequencing is not practical or necessary. Sequencing only the coding regions of the genome enables researchers to focus their resources on the genes most likely to affect phenotype, and offers an accessible combination of turnaround time and price.
How does exome sequencing work?
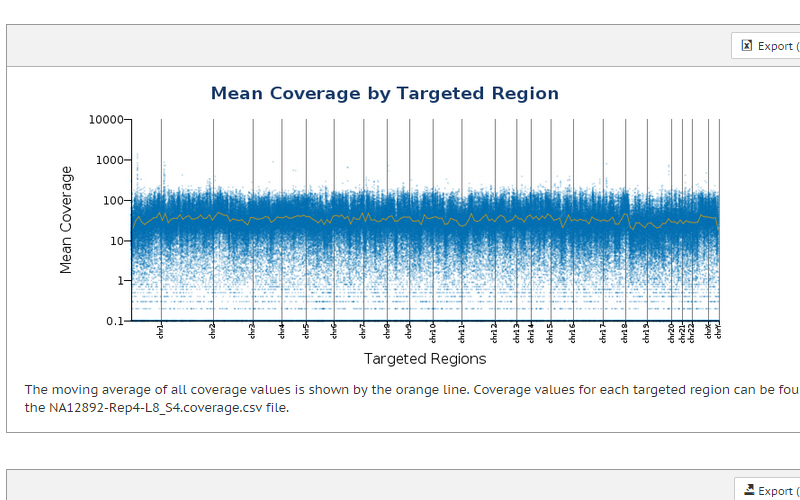
Whole-exome sequencing detects variants in coding exons, with the capability to expand targeted content to include untranslated regions (UTRs) and microRNA for a more comprehensive view of gene regulation. Whole-exome sequencing typically involves using hybrid-capture enrichment approaches to capture the protein-coding sequences. DNA libraries can be prepared in as little as 1 day and require only 4–5 Gb of sequencing per exome.
Recommended whole-exome sequencing workflow
Illumina offers comprehensive exome sequencing workflows that simplify the entire process, from exome enrichment and library preparation to sequencing, data analysis, and biological interpretation.
Library prep
Illumina DNA Prep with Exome 2.5 Enrichment
A fast, integrated whole-exome enrichment and sequencing library preparation kit for a wide range of applications.
Illumina FFPE DNA Prep with Exome 2.5 Enrichment
A sensitive and comprehensive whole-exome sequencing kit for detecting low-frequency variants from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples.
Illumina Custom Enrichment Panel v2
Expand or enhance exome coverage with a custom spike-in panel designed for your targets of interest.
Illumina Cell-Free DNA Prep with Enrichment
A highly sensitive library prep solution to detect low-abundance mutations from cell-free DNA.
Sequencing
NovaSeq X Series
Our most powerful sequencer for ultra-high-throughput projects, featuring up to 16 Tb output and 26 billion single reads per flow cell.
NovaSeq 6000 System
Scalable throughput and flexibility for virtually any genome, sequencing method, and scale of project.
NextSeq 1000 and NextSeq 2000 Systems
User-friendly, flexible, reliable mid-throughput benchtop sequencing for a broad range of current and emerging applications.
Data analysis and interpretation
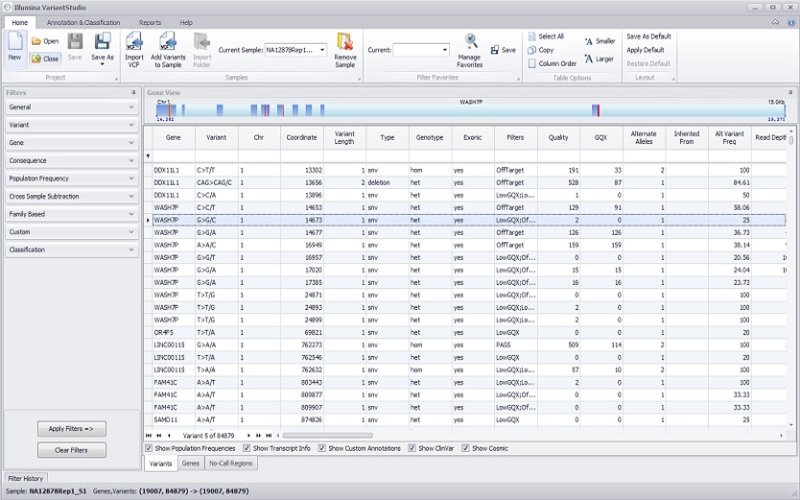
DRAGEN Enrichment App
Push-button alignment, followed by variant calling of Illumina exomes to rapidly identify disease-associated variants.
Emedgene software
High-efficiency data interpretation for germline research whole-exome sequencing, with the support of explainable AI (XAI).
Whole-exome sequencing solutions
Explore comprehensive workflow offerings for whole-exome sequencing, including world-class support from Illumina.
Download brochure
Exome sequencing data analysis
Illumina DRAGEN secondary analysis was developed to address important challenges associated with analyzing NGS data for a range of applications, from whole-exome sequencing to genome and transcriptome sequencing, methylome studies, and more. This software suite rapidly processes NGS data and enables tertiary analysis to drive insights. The available tools make up a highly accurate, comprehensive, and efficient solution that enables labs of all sizes and disciplines to do more with their genomic data.
Learn more about DRAGEN secondary analysisEfficient exome and multiomics data analysis for COPD study
Scientists discuss how DRAGEN pipelines and Illumina Connected Analytics helped them analyze exome sequencing data as well as whole-genome, transcriptome, and metagenome data for a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) research project.
Scientists discuss exome sequencing projects

Implementing whole-exome and targeted sequencing assays
Dr Irina Iordanescu from Regina Maria Genetic Laboratory explains how her lab adopted NGS-based whole-exome and targeted sequencing, and how NGS helped speed up and expand sample processing while reducing costs.
Read article
Using exome and RNA-Seq to study rare genetic diseases
Whole-exome and RNA sequencing prove beneficial in uncovering mutations and pathways associated with rare disease.
Read article
Tumor exomes reveal new insights into cancer biology
Read how researchers perform WES from tumor biopsy samples to better understand tumor onset and progression and identify cancer-related biomarkers.
Read articleEmpowering access for groundbreaking genomic discoveries
Illumina benchtop sequencing systems are making NGS more accessible to laboratories worldwide. Explore a wide variety of applications and methods, from whole-exome sequencing to microbial sequencing, RNA-Seq, single-cell sequencing, and more.
Download eBook
Featured products
Related content
Exome sequencing for cancer research
This method provides useful information about coding mutations associated with tumor progression. By sequencing less than 2% of the genome, it is possible to sequence to higher depth more economically. Learn more about cancer exome sequencing.
Rare disease variant analysis

NGS-based exome analysis can help scientists uncover variants linked to rare and undiagnosed disorders. Learn more about rare disease genomics.
Complex disease genomics
Whole-exome sequencing is a common approach to finding causal variants in cases of complex disorders. Learn more about complex disease research.
RNA exome capture sequencing

Achieve cost-effective, accurate, and sensitive RNA exome analysis of even difficult samples without sacrificing gene fusion discovery power. Learn more about RNA exome capture sequencing.
Additional resources

Gaining insights into novel variants
Regeneron Genetics Center scientists perform exome sequencing on clinical research data sets to identify relevant genetic associations.

DNA sequencing data analysis
Explore user-friendly tools for intuitive analysis of DNA sequencing data.

Genetics of neurological disorders
Researchers use exome sequencing, arrays, and other methods to identify gene variants linked to intellectual disability.

Germline CNV analysis
See a streamlined whole-exome sequencing workflow for germline CNV analysis, from library preparation to insights.
Library Prep and Array Kit Selector
Determine the best kit for your needs based on project type, starting material, and method or application.
Genetic contributions of cognitive control
Exome sequencing helps researchers identify variants for an array designed for ADHD, autism, and schizophrenia studies.

Choosing an NGS company
Seek out a best-in-class NGS company with user-friendly bioinformatics tools and trusted support and service.
Interested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on genomic analysis techniques? Enter your email address.
References
- van Dijk EL, Auger H, Jaszczyszyn Y, Thermes C. Ten years of next-generation sequencing technology. Trends Genet. 2014;30:418-426.
*Data calculations on file. Illumina, Inc., 2015